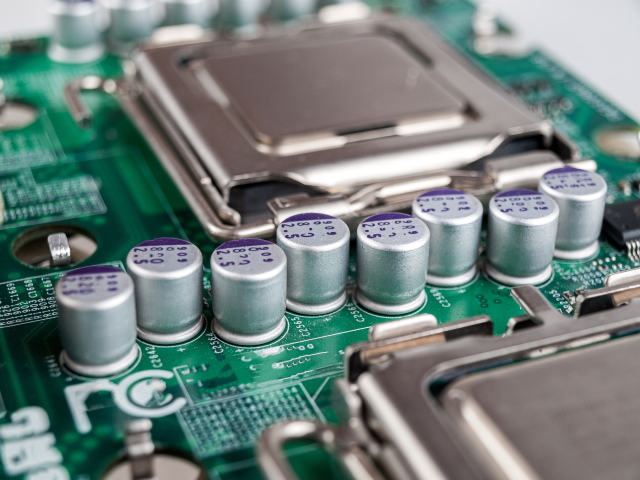
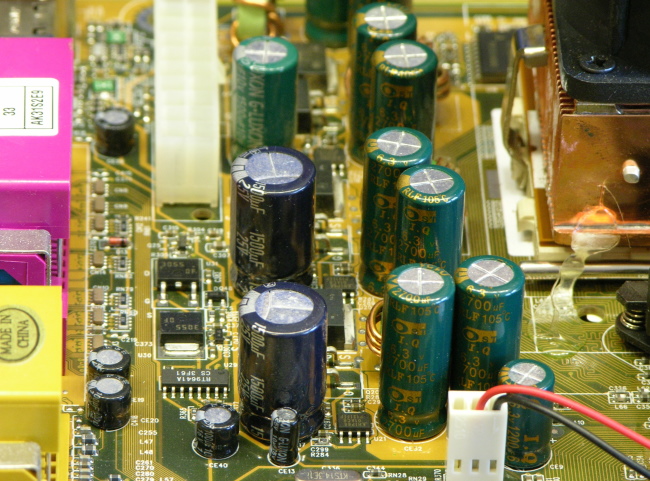
When you’ve got ever been within the cult-like exercise that’s CPU overclocking, one of many phrases that you’d have come throughout an amazing deal is VRM. The time period is ubiquitous within the PC neighborhood, however hardly anybody inside or outdoors the neighborhood really is aware of the way it works. VRM is a type of issues that folks know is essential to the operation of their PCs however appears so mysterious that any additional investigation could be too cumbersome. Because of this we’ve carried out the required analysis and give you this explainer to inform you what’s VRM on the motherboard, the way it works, and the way it impacts your CPU efficiency.
Motherboard VRM: Defined (2022)
On this article, we will likely be exploring the whole lot there’s to learn about VRMs and inform you why they’re so necessary. We’ll see how VRM’s job, whereas easy, is a necessary one, as it’s key to making sure the soundness of the system. In different phrases, it’s effectively price understanding extra about VRM and the way it operates.
Moreover, we may even be how one can differentiate between a good-quality VRM and a foul one. The concept behind that might be to create a fundamental thought of what constitutes a very good VRM configuration, so what to search for the following time you purchase a motherboard.
What Does VRM Stand For?
Earlier than we do a deep dive into how the VRM works, it’s important to grasp what it’s and what the time period stands for. The time period stands for “voltage regulator module”, and it describes an digital circuit that regulates and converts voltages to satisfy the necessities of the CPU, reminiscence, and GPU. It would assist one to think about VRMs as form of like a mini energy provide, similar to your precise principal laptop energy provide that takes 120 or 240 volts from the wall and bumps it all the way down to 12 volts of DC present.
The motherboard VRM in a way does simply that, however for a second time. It takes the 12-volt (DC) output of the ability provide and converts it to sometimes round 1V for a GPU or 1.4 V for a CPU. The opposite necessary job of the VRM is to provide this voltage steadily, with out surges and drops, as it could actually have an effect on the soundness of your complete laptop.
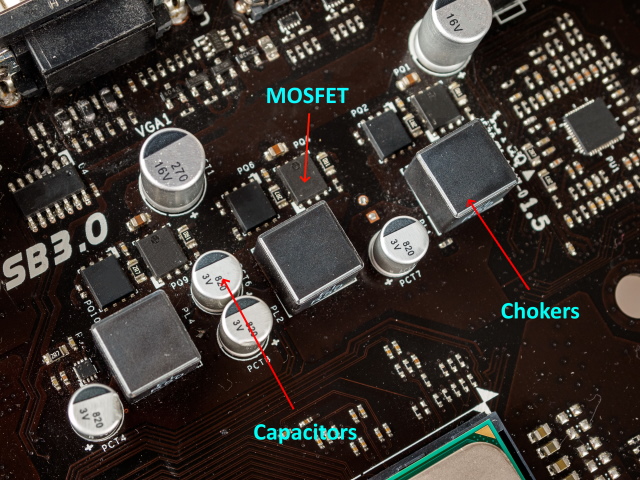
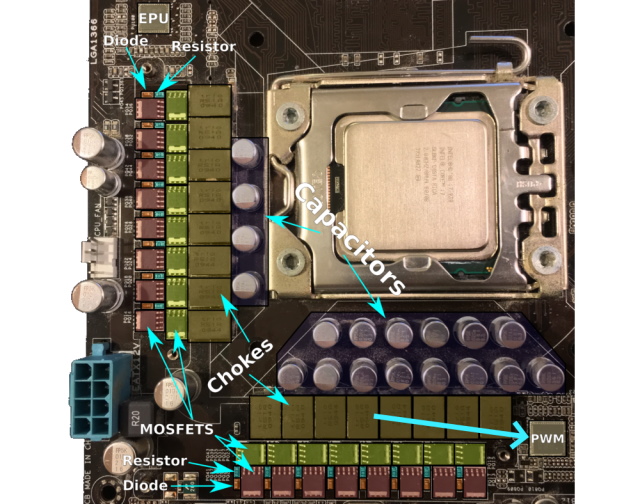
Within the above picture, you possibly can see the structure of the VRM in a contemporary motherboard. It contains three major components: MOSFETs, Chokes, and Capacitors. Most of those are normally positioned underneath heatsinks that encompass your CPU socket and are fairly exhausting to identify. These core elements are accompanied by diodes and resistors, which be certain that the electrical present that arrives at these elements doesn’t exceed sure values.
How Do Motherboard VRMs Work?
The important thing precept on which voltage regulation circuits rely is the flexibility to scale back the typical output voltage of a circuit by switching an enter voltage on and off. So, for instance, when you’ve got a 12V DC enter out of your energy provide, and you turn it on and off for an equal time period, the typical voltage would turn into 6V DC.
However to attain a comparatively steady common voltage, this must occur a number of hundred instances a second. The switching in virtually all the circumstances is achieved by way of a comparatively easy metallic oxide semiconductor subject impact transistor (MOSFET) circuit. However as we are going to see within the subsequent part, the MOSFET doesn’t work alone, however relatively in tandem with different items like chokes, capacitors, and PWM controllers to present the CPU probably the most steady energy doable.
Parts of VRM in Motherboard
MOSFETs
The primary element that we are going to take a look at is the MOSFET, which is basically an insulated gate, a form of change that’s used to amplify or reduce digital alerts. What it does in follow is regulate the passing present, relying on the sign and worth despatched by the PWM controller chip, which is chargeable for managing the ability phases and balancing the alerts (extra on it later).
To higher illustrate this course of, we will take a look at the diagram under. A fundamental VRM circuit consists of two MOSFETs, which on this state of affairs are mainly simply switches, an inductor, and a diode.
The design of VRM MOSFETs can range, however all of them have the identical operate, so we predict it’s not crucial for us to go in-depth and begin explaining some superior electrical engineering. Nevertheless, if you’d like a extra detailed dialogue of every element’s operate, head to WikiChip’s VRM explainer web page. The necessary bit you might want to know is that the voltage conversion begins on the MOSFET, and it’s right here that a lot of the workload occurs.
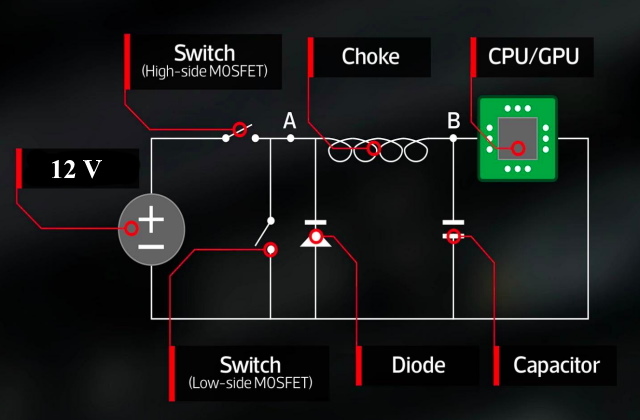
However to elucidate it briefly, the VRM circuit makes use of two MOSFET switches to manage the quantity of voltage that passes to the CPU. When the primary change (high-side MOSFET) is closed, the voltage on the enter of the inductor turns into 12V. This causes the present to begin flowing by way of the choke, which is basically a coil of wire round a magnetic core – slowly elevating the output voltage.
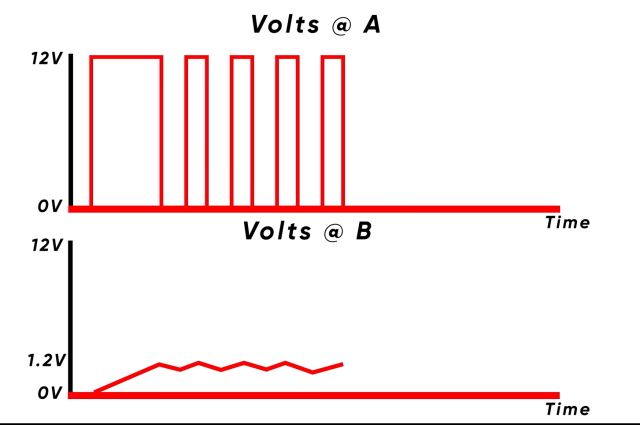
Then, as soon as the specified voltage for the CPU or GPU is reached, the change is closed, which suggests the enter to the choke turns into zero. As {the electrical} provide to the choke drops, the magnetic cost round it dissipates, inducing a voltage in the wrong way (so it’s including to the output voltage relatively than canceling it), which slowly drops off over time. This course of when repeated a number of dozen instances a second provides us a comparatively regular enhance and reduce in voltage (as seen within the voltage determine).
The opposite factor that we’ve to remember about MOSFETS is that each single time it switches on or off, it generates warmth, which will be above about 150 levels Celsius. Which means as you push MOSFETs an increasing number of to their restrict, they have an inclination to warmth up quite a bit. Does this warmth matter? Merely put, it does.
If the VRM MOSFETs get too scorching, it impacts the resistance of the semiconductor, which results in a drop in effectivity, and from there, it’s a endless loop that can solely generate extra warmth. And that is the important thing cause why most MOSFETs in trendy motherboards are coated by cooling options like heatsinks or miniature followers.
Chokes
The following a part of the VRMs that we are going to be is known as Chokes. These are cubic-shaped (though not all the time) inductors usually product of metallic, that are chargeable for changing alternating present (AC) alerts into decrease frequencies or direct present (DC) to be able to stabilize the voltage that comes out of the MOSFET. What does this imply?
Basically, a choke takes the high-frequency energy (12V) coming in from the PWM and turns it right into a steady frequency (1.2-1.4V), so it turns into usable by the CPU and different elements. So, in essence, it serves two features. First, to retailer and filter the ability, and secondly, to manage the general high quality of the ability.
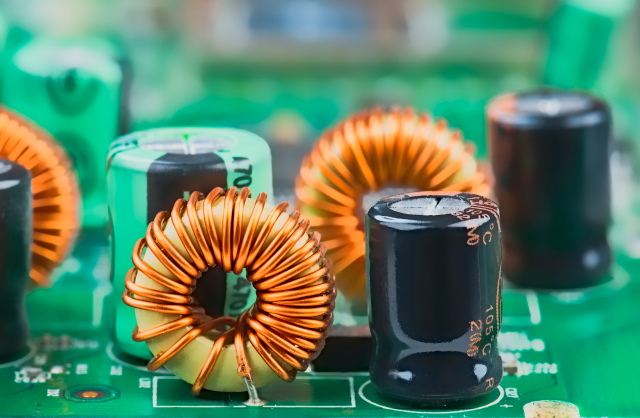
Since chokes play an necessary function within the high quality of energy provided to the motherboard, they’re important in deciding the overclocking capacity. The higher the chokes, the upper the motherboard’s functionality to face up to overclocking. Moreover, every choke on a motherboard additionally represents an influence section. And as a normal rule of thumb, the upper the variety of phases on a motherboard, the extra steady the voltage (extra on this later).
Capacitors
The final core analog element of the VRM that we are going to be exploring is the Capacitor. It’s a frequent electrical element utilized in many digital gadgets to retailer power in an electrical subject, and when required, it could actually discharge this power into the circuit they’re linked to. It acts like a battery in a way, however has larger storage capability for its capacity to quickly output all its power.
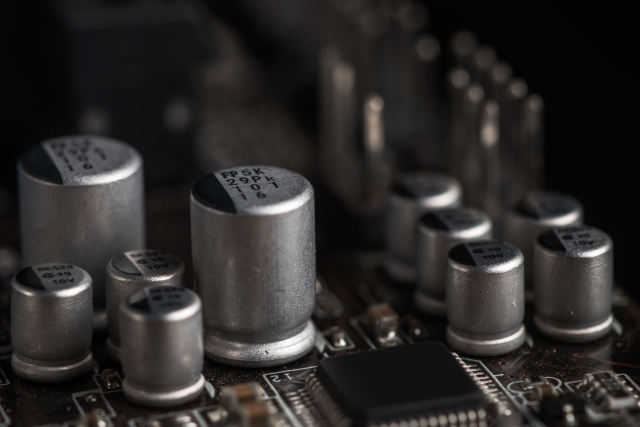
For a VRM and its corresponding energy phases, it serves the identical objective. The capacitors have two principal features within the functioning of the VRM. The primary is to accumulate electrical present, and the second is to retailer and stop voltage surges and cut back ripples within the digital circuit. The concept is to retailer the present obtained from the choke and provide the correct quantity of energy required by the CPU, the remainder is discharged or launched by way of the bottom.
Because of this the capacitor is just not solely an necessary a part of the VRM however relatively an existential necessity. That’s why, for any VRM to be thought of good, it most definitely must make use of high-standard and high-quality capacitors. Often, high-quality capacitors are branded as Stable Capacitors, Hello-C Capacitors, and extra. Within the trendy technology of motherboards, solid-state capacitors are the dominant type of capacitors and have largely supplanted electrolytic ones.
However this wasn’t all the time the case. Within the late Nineteen Nineties and early 2000s, plenty of motherboards, notably, from Taiwanese producers noticed higher-than-expected failure charges of non-solid capacitors. This was largely because of electrolyte composition that triggered corrosion, resulting in excessive ranges of fuel technology, which regularly triggered the capacitors to blow up. This was referred to as the capacitor plague of the early 2000s and is notorious within the PC neighborhood. Whereas the issue was a really sophisticated one, which had a complete host of controversies from industrial espionage to corruption, its bigger implication was that the trade steadily moved from alkaline capacitors to solid-state ones.
PWM Controller
Now that we’ve mentioned the core analog elements of the VRMs, it’s now time to maneuver on to the a part of the circuit that controls the electrical energy movement known as the PWM (pulse width modulation) controller. This controller offers the PWM pulses, that are then fed into the analog a part of the circuit – MOSFETs, Chokes, and so forth.
These PWM controllers, nevertheless, aren’t easy gadgets that simply fireplace out a hard and fast pulse. As an alternative, they’re relatively advanced built-in circuits themselves. Some controllers, notably high-end ones, have a number of section management methods, and so they additionally maintain one other essential operate of the VRM, i.e. monitoring. Furthermore, because the voltage of the CPU or GPU is rarely really fixed, the chip does plenty of work to frequently cut back or enhance the required energy to be able to be extra environment friendly.
So how does it understand how a lot energy to ship? Merely put, it does this by forming a suggestions loop between the CPU and the PWM. The PWM controller takes the reference voltage (VREF) of the CPU, discovered within the motherboard’s BIOS settings, and continually feeds it into the VRM. This voltage is then measured with the present voltage, and if there’s a distinction between the VREF and the precise voltage, the PWM controller modifies the sign to convey the output voltage again in line.
This course of was, until a decade in the past, primarily carried out by analog PWMs, however for probably the most half, have largely been changed by digital PWMs right now. The benefit of digital PWMs is that it opens up the microcontroller to think about a a lot higher vary of different variables and parameters in its voltage correction calculations. These might be temperature sensors, BIOS settings, and different saved values. The draw back to digital PWM controllers is they’re dearer and sophisticated to configure. Fashionable motherboards virtually completely use digital PWMs for CPU and reminiscence energy supply, however analog PWMs are generally used for much less essential elements of a board.
What Are Energy Phases of a Motherboard?
Because the turning on and off of {the electrical} sign by the MOSFET is often carried out a number of hundred instances per second, the voltage can fluctuate greater than the CPU can tolerate. And since it’s already working at such a excessive velocity, it isn’t sensible to attempt switching a complete lot sooner than that. So within the pursuit of higher stability, what we’d like is just not sooner MOSFETs however extra of them in amount.
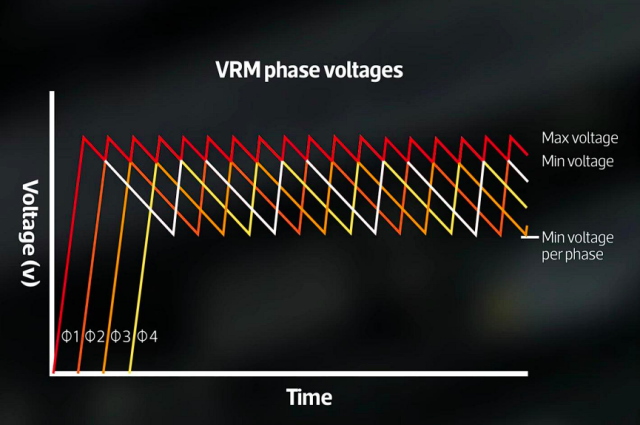
A single VRM circuit will be efficient sufficient for sure functions, however to make sure as easy a voltage supply as doable, you possibly can have a number of VRMs in parallel, creating what we’ve already talked about – a multi-phase VRM (the picture above represents a multi-phase VRM). How does this work?
From the above diagram, you possibly can see that if every section of the VRM is staggered simply in the appropriate approach, the phases distribute the power load over a wider variety of elements. Not solely does this present the CPU or GPU with smoother energy, because the time between energy pulses will be decreased, but additionally helps in lowering warmth manufacturing and stress on elements.
You’ll usually see motherboard producers promote excessive numbers of phases in an A+B format, like 8+3 or 6+2. So, what does this imply? In principle, it’s easy sufficient. The primary quantity is the variety of phases devoted to the CPU, whereas the second is the variety of phases devoted to different elements of the motherboard like reminiscence.
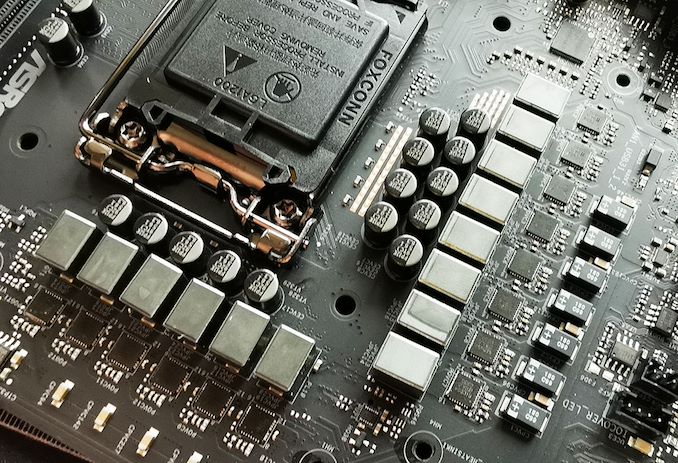
It’s on this context that you simply is likely to be tempted to suppose that extra phases equal smoother energy supply. That is true to a sure level. For instance, entry-level boards normally have three or four-phase CPU energy, whereas higher-quality boards can have six to eight. Nevertheless, the place it will get sophisticated is when motherboard producers say a board has, as an illustration, a 16+2 design, however could in truth be utilizing a doubler and solely have a real 8-phase setup.
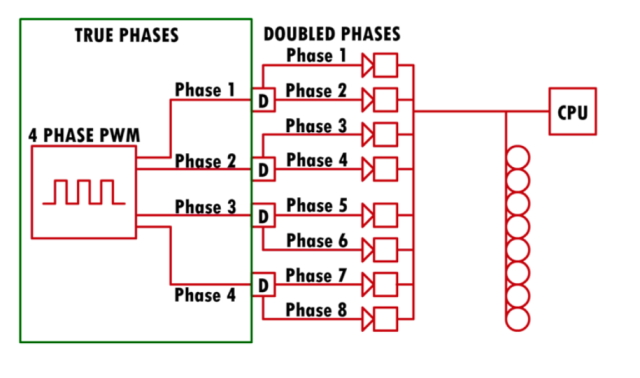
A doubler lets you multiply the advantage of present phases with out together with further phases on the board. The online result’s an analogous discount in total load and warmth technology as a traditional multi-phase circuit, mentioned above, however solely with a voltage ripple discount of half the circuits. That mentioned, although, the general advantage of bigger numbers of phases is relatively diminishing. So you’ll get a extra dependable motherboard in a way, however because the energy supply {hardware} is basically much like a decrease section one, it’s going to most likely not overclock as effectively.
Moreover, a number of phases even have one other profit. Say you may have a CPU that requires 100 amperes to run with a single section. So, all 100 amperes must go instantly by way of these elements. However with two phases, solely 50A goes by way of every section, which signifies that elements with a decrease ranking can be utilized, and these elements are normally cheaper. This permits producers to make 4-phase VRMs at a less expensive price than, let’s say, in the event that they needed to make a 2-phase VRM with higher high quality elements.
Can the High quality of VRM Affect CPU Efficiency?
The query that almost all laptop customers have about VRMs is – How does VRM have an effect on my system’s efficiency? Fact be informed, the standard of VRM won’t have the impression of, for instance, getting a brand new $600 graphics card in your system. However the high quality of your VRMs can make an enormous distinction on the subject of the longevity and stability of your system.
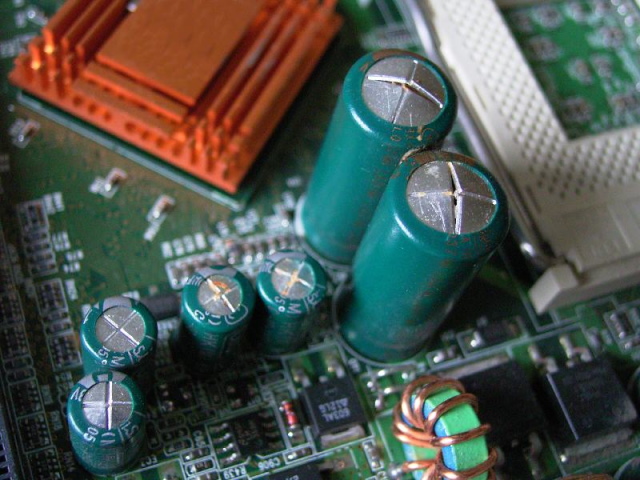

It is because cheaply-made VRMs can begin to fail over time, and it could actually result in system instability and even crashes at inventory speeds. Moreover, a poor-quality VRM can mess up the ability supply of your motherboard to the purpose the place it may injury different costly elements.
And at last, when you ever wish to begin overclocking on a bad-quality motherboard, say goodbye to that dream, because you received’t get far with a poorly designed VRM module. Why? As a result of as you push your PC throughout overclocking, you require high-level management on the subject of voltages, which may solely be offered by higher-quality VRMs.
How Can You Inform If Your VRM Is as much as the Process?
You have to be your motherboard and asking your self, how do I make it possible for my VRM is as much as the duty of overclocking and received’t concurrently combust once I push the voltages a bit of bit? Deciphering a motherboard’s VRMs is usually a bit tough, however one of many best issues you are able to do is simply rely the variety of chokes you see on the motherboard.
As we’ve already talked about, every choke in your motherboard corresponds to 1 energy section, and normally, all however one or two of those chokes across the CPU socket are reserved for CPU cores. Because of this when you’ve got a motherboard with many chokes, it most likely has plenty of phases that may cut up the overclocked voltage, lightening the load on every section.
So when you’ve got a motherboard with three or 4 phases for the CPU, it’s most likely an entry-level board. Which means it’s most likely not suited to ultra-high-performance chips. However when you’ve got six, eight, or much more phases in your motherboard, it’s most likely a high-end board that shouldn’t have any downside retaining your system steady even underneath load.
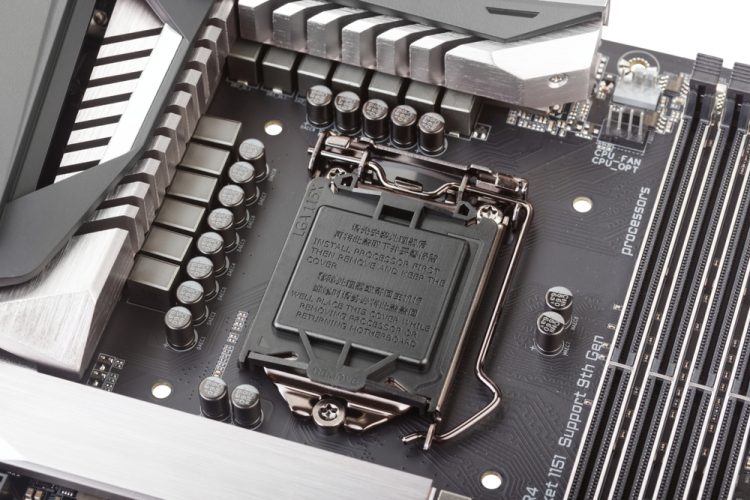

Moreover, it’s additionally a good suggestion to see in case your motherboard comes geared up with solid-state capacitors or low cost liquid-based capacitors that include conducting liquid. Liquid capacitors (electrolytic) could cause issues to the system if they aren’t constructed correctly. And even when they’re made appropriately, they’ve a excessive likelihood to bulge, rupture, and even explode over time.
The place it will get sophisticated is when producers say your motherboard has, as an illustration, a 16+2 design, however the board could in truth be utilizing doublers and solely has a real 8-phase setup. Discovering out the precise setup can take a little bit of sleuthing, both looking out on-line sources which have already carried out the digging or wanting up the PWM chips and discovering out what number of phases are literally rated to deal with the load.
If the chip solely has 4 or eight phases, and the board claims 16, clearly some doubling is happening. For most individuals, it received’t be a priority come what may, however if you’re in search of a critical aggressive benefit in overclocking, a sturdy VRM setup is essential.
So must you be fearful in case your motherboard has solely 4 phases? Nicely, it relies on which processor you might be utilizing. If it’s a modern-day mid-range CPU like an Intel Core-i3/ i5 (Eighth-Gen or later) or an AMD Ryzen processor, it must be simply nice. CPUs have gotten to some extent the place they will accomplish that far more with a lot much less energy. And because the trade is shifting in direction of extra power-efficient chips, the times of the high-numbered energy phases are coming to an finish. However if you’re somebody who needs to improve to a high-performance/ overclockable chip, it might be very best in case your motherboard has a better variety of energy phases.
Why Good VRMs Are Required for Overclocking?
Whereas the quantity of VRMs, their measurement, and the variety of energy phases supported by your motherboard is a crucial issue, it doesn’t have a big impact in your day-to-day efficiency. It does, nevertheless, matter for lovers, players, and different professionals who wish to overclock your CPU. That is as a result of overclocking instantly places a burden on the VRM, as growing the voltage is important on the subject of {hardware} overclocking. As an increasing number of voltage is run by way of the system, regulating it turns into an more and more tougher job.
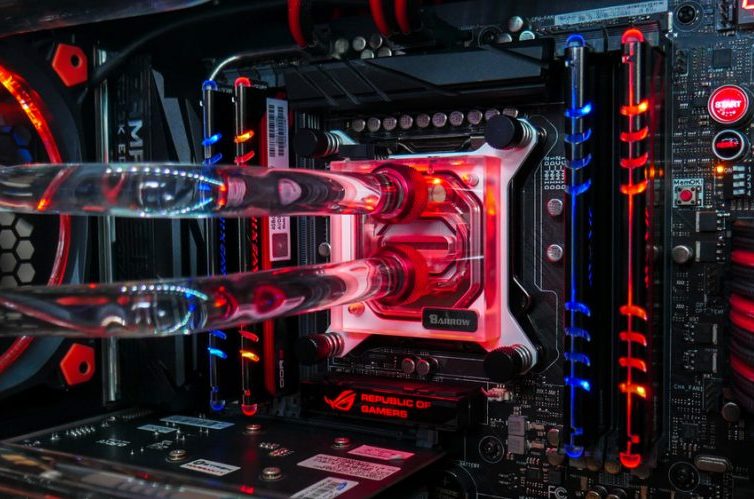

That is the state of affairs the place the whole lot from the variety of phases to the dimensions of your heatsink and the standard of capacitors begins to matter. And it is for that reason that high-level overclocking is reserved for less than the perfect of motherboards. These motherboards not solely have a excessive variety of energy phases however are additionally constructed with premium sub-components like solid-state capacitors which have the aptitude to face up to a excessive quantity of voltage and present. Furthermore, these motherboards are additionally armed to the enamel with good cooling setups, as some even have lively cooling, which incorporates small followers and even liquid cooling blocks.
VRMs: Ceaselessly Requested Questions
The right way to Discover If My Motherboard Has Stable Capacitors? What Are Its Benefits?
The best technique to see which capacitors the motherboard in your PC has is to bodily take a look at them. Visually, the capacitors look very totally different as they each have elementary designs. The solid-state capacitors are normally smaller in measurement compared to electrolytic capacitors.
You may simply spot the distinction within the comparative picture under, the place the motherboard within the first picture was designed utilizing solely solid-state capacitors, and the motherboard within the latter picture makes use of the extra frequent and cheaper electrolytic capacitors.
Stable capacitors and electrolytic capacitors retailer electrical energy and discharge it when wanted. The distinction, nevertheless, is that strong capacitors include a strong natural polymer, whereas electrolytic capacitors use a typical liquid electrolyte, therefore, the distinction in names.
So how does this have an effect on the capacitor’s efficiency? By way of lifespan, strong capacitors last more than electrolytic capacitors, particularly at decrease working temperatures. In some circumstances, solid-state capacitors can final greater than 6 instances longer than electrolytic ones. If one have been to transform this distinction in precise years, the strong capacitor would final roughly 23 years, whereas the electrolytic capacitor would die after solely three years.
Moreover, strong capacitors additionally have a better tolerance not just for larger temperatures, however additionally they carry out higher with larger frequencies and better present than electrolytic capacitors. And lastly, in contrast to their counterparts, the strong capacitors don’t have any likelihood of exploding, as there are not any liquid elements of their physique. All of this, together, makes them far more suited to excessive stress operations, which may embody overclocked setups or workstations.
Which Motherboard Ought to I Get for Overclocking?
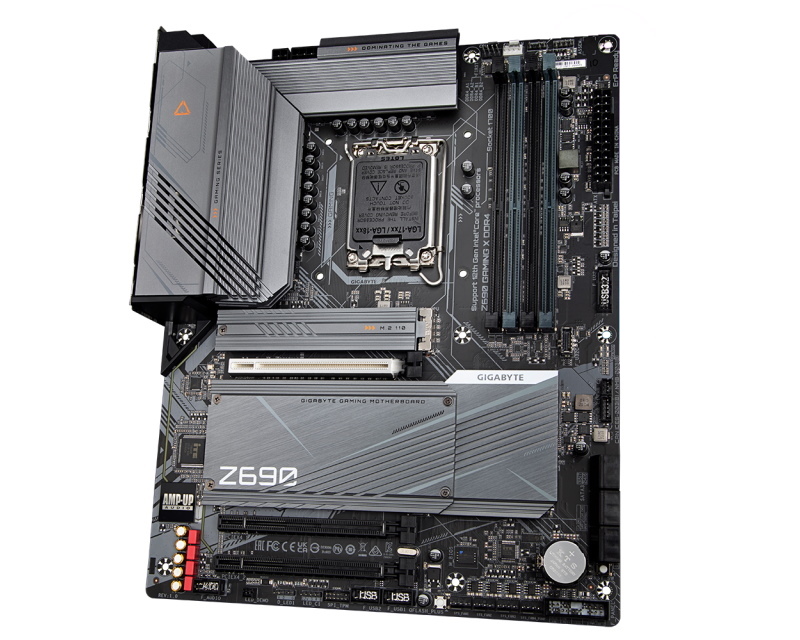

Shopping for a motherboard is already a posh choice because the market is full of totally different socket sorts and kind components. It’s additional made extra sophisticated when you intend to purchase a very good motherboard for overclocking, as not all boards are as much as the duty. However when you’re in search of a very good motherboard to overclock your system with, there are some issues that it’s best to bear in mind.
Firstly, motherboards that assist high-level overclocking are ones that supply a sturdy energy supply system. Why? That’s as a result of working a CPU at a better clock velocity requires one to push extra energy by way of it. So, for instance, if you wish to overclock a 125W CPU that has a max clock velocity of 4.5 GHZ, to run it at 5 GHZ, you will have to pump in additional than 125W.
As the quantity of voltage and energy necessities enhance, it places a major quantity of stress on the VRMs. On this case, having a better variety of energy phases will assist as every energy section will be capable of divide the workload between them. Say there’s a load of 100 amperes on a single energy section, having a second energy section will cut back the burden to 50 amperes (50A).
That is the explanation why most high-end motherboards have extra energy phases. So, if you’re planning to overclock your CPU to its restrict, within the course of of accelerating voltages, we recommend in search of a motherboard with a minimum of 8 energy phases. Moreover, you also needs to search for a motherboard with a sturdy cooling setup as larger voltages additionally imply extra warmth.
As we’ve already mentioned above, MOSFET switches create a major quantity of warmth every time they activate or off, and that is additional amplified if you’re speaking about an overclocked chip. A very good cooling setup in an overclocked system is just not a luxurious, however a necessity.
What Are VRMs and Why Are they Vital?
In essence, VRMs are a sophisticated topic, as they take care of plenty of technical jargon {that a} common PC fanatic would by no means come throughout (PWM, MOSFETS, chokes, and so forth.). It’s this technicality that forestalls most laptop customers from ever partaking with it like they do with CPUs or GPUs. However as we’ve seen on this article, the VRMs, whereas advanced, kind the very coronary heart of recent computing. Understanding them is a key to uncovering the various reified objects of our on a regular basis lives.
We hope that you simply have been in a position to perceive a bit extra about VRMs and grew a brand new appreciation for them, for they’re a marvel of recent engineering. Additionally, you’ll now admire overclocking extra after going by way of this text. Moreover, we hope this information helped you get a greater grasp on how a VRM can impression your on a regular basis PC, and within the course of, made you much more conscious of what to search for when shopping for a brand new motherboard in your PC. When you’ve got additional questions on how particular elements of the motherboard work, verify our detailed overview linked right here.















